CI & CD
Continuous Integration Explained
Continuous Integration (CI) is an automated process that integrates source code changes and merges all developer working copies into a shared mainline several times a day. The feedback loop is part of this process.
In the past, developers on a team might work in isolation for an extended period of time and only merge their changes to the master branch once their work was completed. This made merging code changes difficult and time-consuming, and also resulted in bugs accumulating for a long time without correction. These factors made it harder to deliver updates to customers quickly.
CI keeps the master branch clean. Teams can leverage modern version control systems such as Git to create short-lived feature branches to isolate their work. A developer submits a “pull request” when the feature is complete and, on approval of the pull request, the changes get merged into the master branch. Then the developer can delete the previous feature branch. Development teams repeat the process for additional work. The team can establish branch policies to ensure the master branch meets desired quality criteria.
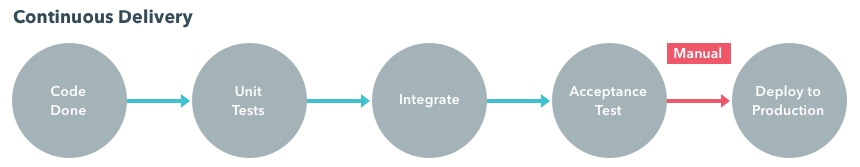
Continuous Delivery Explained
Continuous Delivery (CD) is an extended Continuous Integration process with additional steps, producing an installable outcome of the software or a delivery package (which can be a binary file, a zip archive or an installer executable). This process works if you don’t rely on automated tests and you need to control when software is shipped to production.
Continuous Deployment Explained
Continuous Deployment is an extended Continuous Delivery process with additional steps automating deploying to staging and production.
Worth Reading
Last updated